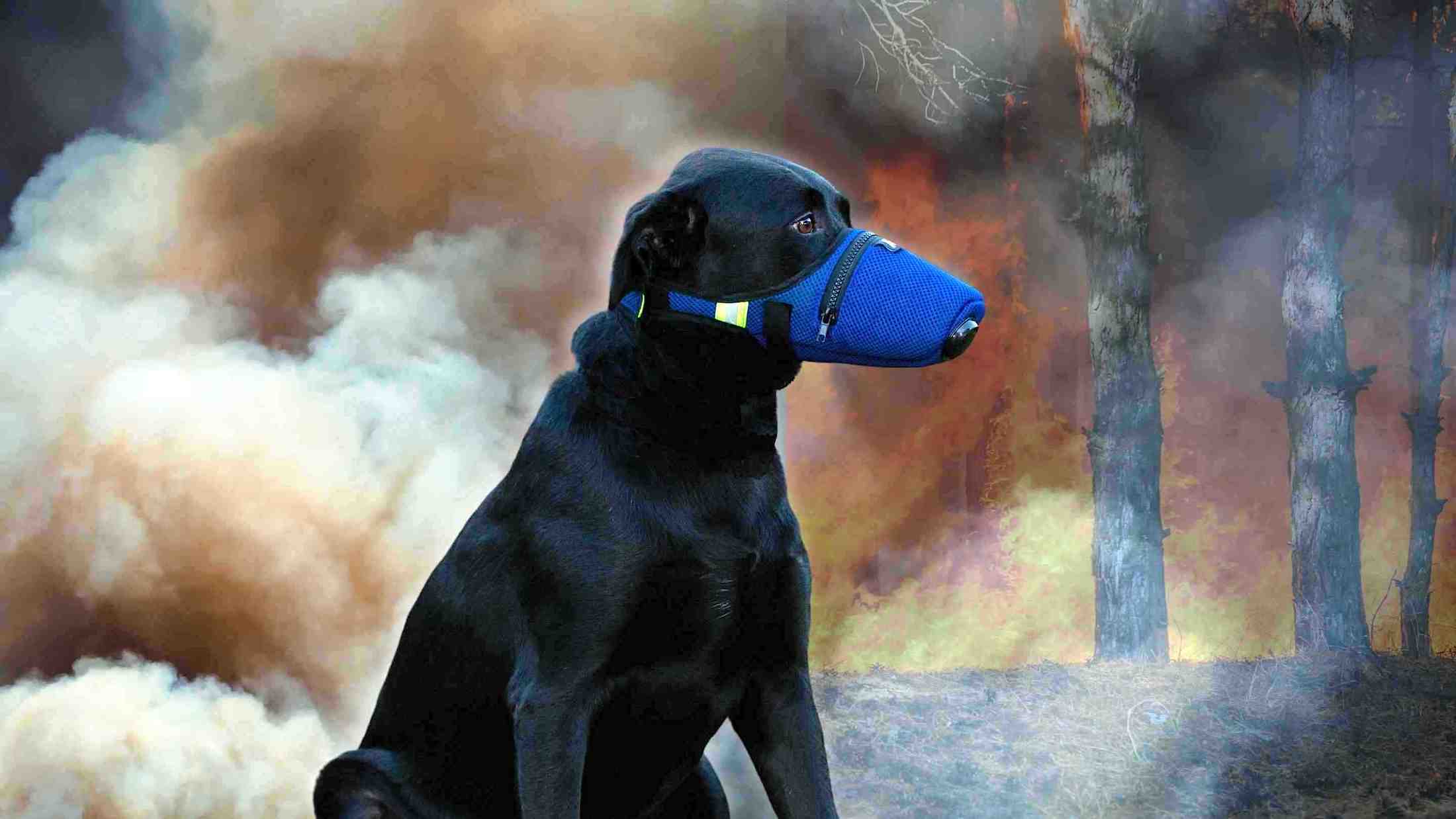
As pet owners, we strive to keep our furry friends healthy and happy, but we may not always be aware of the environmental factors that can impact their health. One such factor is the presence of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in our homes and surroundings. One example is the Ohio train derailment last week causing great concern about the chemicals from the tanks spilling into the ground and burning from their containers.
VOCs are a type of indoor or outdoor air pollutant that can be harmful to both humans and pets, including dogs. In this blog article, we will explore the impact of VOCs on dog health, including the potential health effects of exposure and how we can take steps to reduce the risk of harm to our four-legged companions.

What is VOC?
VOC stands for Volatile Organic Compounds. These are a group of chemicals that are commonly found in many household and industrial products, such as cleaning supplies, paints, and solvents. VOCs can easily evaporate into the air at room temperature, and they can have both short-term and long-term health effects.
Exposure to VOCs can cause a variety of symptoms, including eye, nose, and throat irritation, headaches, dizziness, and fatigue. Some VOCs, such as benzene and formaldehyde, have been linked to cancer and other serious health problems.
Because of the potential health risks associated with VOCs, many governments have established regulations to limit their use in certain products, and there are also VOC emissions standards for indoor air quality. It is important to follow proper safety protocols when using products that contain VOCs, such as using them in well-ventilated areas or wearing protective gear.

Coarse Particle Size:
PM10: inhalable particles, with diameters that are generally 10 micrometers and smaller
|
Fine Particle Size:
PM2.5: fine inhalable particles, with diameters that are generally 2.5 micrometers and smaller.
|
Ultrafine Particle Size:
PM1.0: Ultrafine particles are also referred to as nanoparticles (nm).
|
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) can potentially affect the health of dogs in similar ways as they can affect humans. Like humans, dogs can breathe in VOCs, which can then be absorbed into their bloodstream and distributed throughout their body. The health effects of VOCs on dogs can depend on many factors, including the specific type and concentration of VOCs, the duration and frequency of exposure, and the individual dog's health and sensitivity.
Some of the potential health effects of VOC exposure in dogs can include:
-
Respiratory problems: Exposure to some VOCs, such as formaldehyde or benzene, can increase the risk of respiratory problems in dogs, including coughing, wheezing, and difficulty breathing.
-
Allergic reactions: Some dogs may be allergic to certain VOCs, which can cause skin rashes, hives, or other allergic reactions.
-
Neurological effects: Long-term exposure to some VOCs, such as toluene or xylene, can increase the risk of neurological effects, such as confusion, tremors, or nervous system damage.
-
Liver and kidney damage: Certain VOCs, such as carbon tetrachloride or trichloroethylene, can cause liver or kidney damage in dogs.
-
Developmental and reproductive effects: Some VOCs, such as benzene or toluene, can increase the risk of developmental or reproductive effects in dogs, such as birth defects or fertility problems.
It's important to note that the risk of health effects from VOC exposure in dogs can depend on many factors, and some dogs may be more sensitive to VOCs than others. If you are concerned about potential exposure to VOCs and your dog's health, it's important to consult with a veterinarian and take steps to reduce or eliminate exposure, such as using products with low VOC content, increasing ventilation, or using protective equipment.

What types of VOC are common in personal workshops at home?
Personal workshops at home can contain a variety of sources of volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Some common sources of VOCs in personal workshops at home may include:
-
Paints and solvents: Many paints and solvents used for DIY projects, such as oil-based paints, lacquers, and thinners, contain VOCs.
-
Adhesives and glues: Many adhesives and glues used for DIY projects, such as epoxy, contact cement, and construction adhesives, contain VOCs.
-
Wood and wood finishes: Wood and wood finishes, such as stains, varnishes, and sealers, can release VOCs into the air.
-
Cleaning products: Many cleaning products used in workshops, such as degreasers and solvents, can contain VOCs.
-
Combustion engines: Combustion engines, such as those found in generators, lawn mowers, and other tools, can produce VOCs as a byproduct of combustion.
-
3D printing: Some 3D printing materials, such as acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS) and polycarbonate (PC), can release VOCs when heated.
To reduce exposure to VOCs in personal workshops at home, it is important to use products with low VOC content when possible, to provide good ventilation to the workspace, and to use protective equipment such as gloves, goggles, and respirators as needed. It is also important to follow product instructions for use and disposal to minimize exposure.

What do scientists recommend for people and pets to protect themself from VOC?
Scientists typically recommend several measures to help people protect themselves from volatile organic compounds (VOCs), including:
-
Ventilation: Proper ventilation is one of the most effective ways to reduce exposure to VOCs. This can be accomplished by opening windows and doors, using exhaust fans, and ensuring that air filters in heating and cooling systems are clean and functioning properly.
-
Reduce indoor sources of VOCs: Many VOCs come from common household products such as paints, cleaning supplies, and air fresheners. Choosing products with low VOC content or switching to natural cleaning products can help to reduce exposure.
-
Use protective equipment: When working with or around VOCs, using protective equipment such as gloves, goggles, and respirators can help to reduce exposure.
-
Testing: Home air quality testing can help to identify potential sources of VOCs and provide recommendations for reducing exposure.
-
Avoid tobacco smoke: Tobacco smoke is a major source of VOCs, and exposure to secondhand smoke can increase the risk of many health problems.
-
Follow product instructions: Always follow product instructions for use and disposal to help minimize exposure to VOCs.
In addition, scientists recommend staying informed about potential sources of VOCs and taking steps to minimize exposure where possible. If you have concerns about potential exposure to VOCs and are experiencing any symptoms or health problems, it's important to seek medical attention and consult with a qualified health professional.

Should a dog wear an N95 air filter mask to protect against volatile organic compounds?
An N95 air filter mask is primarily designed to protect the wearer from airborne particles, such as those found in dust, smoke, and other forms of air pollution, but it may also provide some protection against certain types of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) found in the air. However, whether or not an N95 mask is sufficient for protection against VOCs will depend on several factors, including the concentration of the VOCs in the air, the duration of exposure, and the type of VOCs.
In some cases, wearing an N95 mask may be an effective way to reduce exposure to certain VOCs in the air, particularly those that are present in smoke, smog, or other forms of air pollution. However, for specific industrial or lab-related activities, an N95 mask may not be enough and a higher level of protection such as a respirator with a chemical cartridge may be required.
It's important to note that wearing an N95 mask is not a substitute for other protective measures that should be taken to limit exposure to VOCs. Proper ventilation, appropriate work practices, and other engineering controls should also be used to reduce the risk of exposure.
How does a K9 Mask® dog air filter protect a dog from VOC?
A K9 Mask® air filter designed for dogs is effective at protecting a dog from some VOC, but not all. As mentioned above an N95 air filter is partially effective at filtering VOC. Another important factor is activated carbon. All air filter types used in the K9 Mask® have a layer of activated carbon.

Activated carbon air filters are designed to help protect from volatile organic compounds (VOCs) by filtering them out of the air that is breathed in. Activated carbon is a type of carbon that has been treated with oxygen to open up millions of tiny pores between the carbon atoms. These pores create a large surface area that can trap and absorb pollutants, including VOCs, as air passes through the filter.
When activated carbon air filter masks are worn, the air that is breathed in passes through the filter, which contains layers of activated carbon. The activated carbon in the filter traps the VOCs as they pass through, preventing them from reaching the person's lungs. The effectiveness of activated carbon air filter masks in protecting against VOCs can depend on many factors, including the type and concentration of VOCs in the air, the quality of the filter, and the fit of the mask to the person's face.
It's important to note that while activated carbon air filter masks can be effective in reducing exposure to VOCs, they may not provide complete protection, especially if the VOC concentration is high. In addition, wearing a mask is just one of several steps that can be taken to reduce exposure to VOCs, such as using products with low VOC content, increasing ventilation, and using protective equipment such as gloves and goggles. It is important to follow safety guidelines and use the appropriate protection when dealing with high levels of VOCs to minimize exposure and associated health risks.